Introduction
Bacteria are microscopic organisms that come in various shapes and arrangements, playing crucial roles in ecosystems, medicine, and industry. Understanding bacterial morphology is essential for microbiologists, researchers, and healthcare professionals. This guide explores bacterial shapes, structural arrangements, and their biological significance.
Understanding Bacterial Morphology
Bacterial morphology refers to the shape and structure of bacterial cells. These characteristics help scientists classify bacteria and determine their functions. The primary bacterial shapes include:
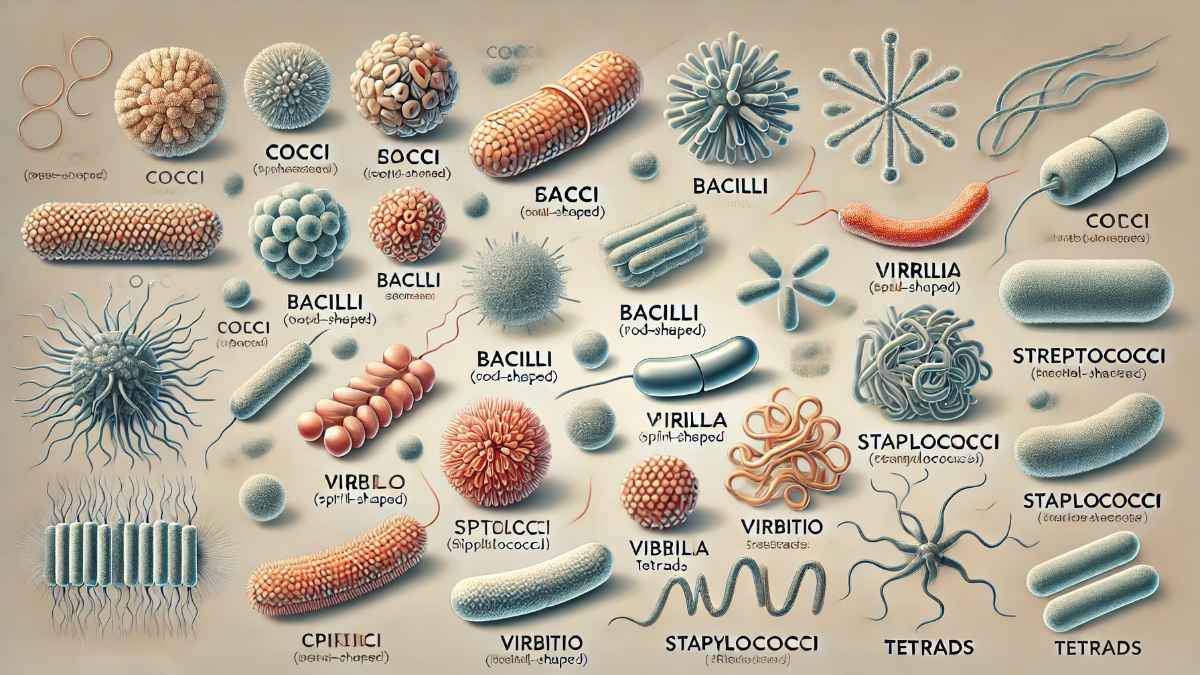
Major Shapes of Bacteria
1. Cocci (Spherical Bacteria)
- Round or oval-shaped.
- Common examples: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae.
2. Bacilli (Rod-Shaped Bacteria)
- Cylindrical and elongated.
- Examples: Escherichia coli, Bacillus anthracis.
3. Spirilla (Spiral-Shaped Bacteria)
- Helical or corkscrew-like.
- Examples: Spirillum volutans, Helicobacter pylori.
4. Vibrio (Comma-Shaped Bacteria)
- Curved, resembling a comma.
- Example: Vibrio cholerae.
5. Filamentous Bacteria
- Thread-like structures forming networks.
- Example: Actinomyces.
Common Bacterial Arrangements
Bacterial cells can organize into distinct arrangements based on their division patterns.
Types of Bacterial Arrangements
1. Diplococci and Diplobacilli
- Pairs of cocci or bacilli.
- Example: Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
2. Streptococci and Streptobacilli
- Chains of cocci or bacilli.
- Example: Streptococcus pyogenes.
3. Staphylococci
- Clustered cocci resembling grape-like structures.
- Example: Staphylococcus aureus.
4. Tetrads and Sarcina
- Groups of four or eight cells.
- Example: Micrococcus luteus.
Importance of Bacterial Shapes and Arrangements
Understanding bacterial morphology helps in:
- Medical Diagnosis: Identifying bacterial infections.
- Antibiotic Treatment: Targeting specific bacterial types.
- Industrial Applications: Fermentation, bioremediation, and food production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What determines the shape of bacteria?
Bacterial shape is influenced by the cell wall composition and genetic factors.
Why do bacteria have different arrangements?
Arrangements occur due to variations in cell division and adhesion properties.
How do bacterial shapes affect their function?
Different shapes allow bacteria to adapt to environments, aiding in movement, survival, and pathogenesis.
Can bacteria change their shape?
Some bacteria exhibit pleomorphism, meaning they can change shape under specific conditions.
Are all bacteria harmful?
No, many bacteria are beneficial and essential for processes like digestion and environmental balance.
How do scientists classify bacteria based on shape?
Using microscopic analysis, staining techniques, and genetic sequencing.
Conclusion
Bacterial shapes and arrangements are fundamental in microbiology, influencing their behavior, function, and impact on human health. Understanding these variations is crucial for medical science, biotechnology, and environmental studies.