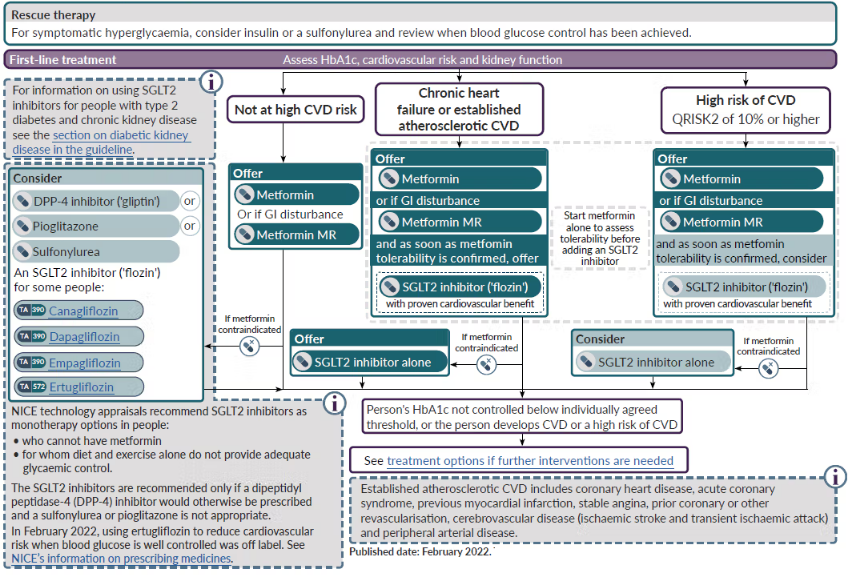
Introduction
Metformin is often the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, but over time, some patients may need additional support to maintain stable blood sugar levels. When to switch from metformin to insulin is a crucial decision based on various factors, including blood sugar control, A1C levels, and overall health. In this guide, we’ll discuss the key signs indicating a transition, how the switch works, and expert recommendations to help you manage diabetes effectively.
Why Metformin May No Longer Be Enough
How Metformin Works in Diabetes Management
Metformin helps lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver. However, as type 2 diabetes progresses, the body’s insulin production may decline, making metformin alone insufficient.
Key Signs It’s Time to Switch from Metformin to Insulin
Persistently High A1C Levels
- If your A1C level remains above 8% despite metformin and lifestyle modifications, insulin may be required.
Consistently High Fasting Blood Sugar
- If your fasting glucose levels remain above 180 mg/dL despite increasing your metformin dosage, insulin therapy might be necessary.
Frequent Hyperglycemia Symptoms
- Experiencing excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision despite metformin treatment suggests your body needs additional insulin support.
Significant Weight Loss or Muscle Wasting
- Unexplained weight loss and muscle breakdown may indicate that your body isn’t using glucose efficiently, necessitating insulin therapy.
Development of Diabetes-Related Complications
- If you experience nerve damage, kidney disease, or vision issues, better blood sugar control with insulin might be required.
Making the Switch: What You Need to Know
How Insulin Therapy Works
Insulin helps regulate blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. It comes in different types, including:
- Rapid-Acting Insulin – Works quickly after meals.
- Long-Acting Insulin – Provides 24-hour coverage.
- Premixed Insulin – A combination of rapid and long-acting insulin.
Steps to Transition from Metformin to Insulin
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
- A doctor will assess your current condition and determine the best insulin regimen.
Start with a Low Dose
- Most patients begin with long-acting insulin at bedtime while continuing metformin.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
- Frequent monitoring ensures proper dosage adjustments and stable glucose control.
Adjust Diet and Lifestyle Accordingly
- A balanced diet, exercise, and medication adherence are essential for smooth transitioning.
Managing Diabetes After Switching to Insulin
Tips for Successful Insulin Therapy
Understand Insulin Timing
- Take insulin at the right times to prevent blood sugar spikes.
Rotate Injection Sites
- Avoid injecting in the same spot repeatedly to prevent skin issues.
Recognize Hypoglycemia Symptoms
- Shakiness, dizziness, and confusion can signal low blood sugar, requiring quick intervention.
Keep a Diabetes Journal
- Tracking food intake, insulin doses, and glucose levels can help optimize management.
FAQ Section
Frequently Asked Questions About Switching from Metformin to Insulin
1. Will I have to stop metformin completely when switching to insulin?
Not necessarily. Some patients continue metformin alongside insulin for better blood sugar control.
2. How long does it take to adjust to insulin therapy?
Most people adapt within a few weeks, but dosage adjustments may take longer based on individual responses.
3. Does insulin cause weight gain?
Insulin can lead to weight gain, but a healthy diet and exercise can help minimize this effect.
4. Can I reverse the need for insulin?
In some cases, significant lifestyle changes may reduce insulin dependency, but it depends on diabetes progression.
5. How do I prevent hypoglycemia when taking insulin?
Monitor blood sugar levels, eat balanced meals, and adjust insulin doses as needed to avoid low blood sugar episodes.
6. Are there alternatives to insulin if metformin stops working?
Other medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors may be considered before switching to insulin.
Conclusion
Switching from metformin to insulin is a significant step in diabetes management. If your current treatment isn’t effectively controlling blood sugar, insulin therapy can provide better regulation and prevent complications. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes, and focus on a healthy lifestyle to enhance your diabetes management. By understanding the right time and method for transitioning, you can maintain optimal health and well-being.